Introduction
Stroke is an emerging important health problem in our society. Ischemic stroke is the third major cause of death, causes more hospitalization with disability. With the occurrences of newer therapies, acute ischemic stroke has a higher hope for quick recovery and better outcome. Despite novel therapies, poor prognosis may still happen because ischemic stroke is a heterogeneous disease in which result is influenced by several factors. The risk factors specifically blood pressure (BP), alcohol, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidaemia and smoking predict the occurrences of stroke. Outcome is further influenced by genetic predisposition, temperature, glucose and other unknown factors but still they are not completely responsible, therefore there is a continuous dispute and search for prediction of occurrence of stroke and reliability of prognostic markers in stroke have acquired interest in current years.
Inflammatory process plays an important role in pathophysiology of stroke. There is a production of proteins called acute Phase Proteins, when the individual is exposed to any insult such as infection and injury. This acute phase protein (APP) is elevated in both acute and chronic inflammatory states. The acute phase reactants are fibrinogen, ferritin, haptoglobin, hsCRP, Complements (C3), Complements (C4) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF).
Many studies shown that iron plays a major role in neurotoxicity and oedema formation after stroke. Ferritin is a major cellular iron storage protein. In brain tissue most of the non-heme iron is in the form of ferritin which is located in astrocytes and microglia. In cerebrovascular disease the oxygen free radicals increase the volume of iron in the cytosol during oxidative stress by enabling the release of iron from ferritin. Ferrous iron mediated free radical mechanisms assumed to play a major role in acute stroke. Ferritin is also considered as an acute phase reactant. Therefore, elevation of acute phase reactant indicate inflammatory burden and it gets elevated in vascular events. Although several studies were done it is very difficult to assess the prognosis of stroke. Several indicators like site of infarction, size of infarct, vessel involved, Glasgow coma scale (GCS) and oedema around the infarct to assess the severity and prognosis of ischemic stroke and in haemorrhagic stroke it includes Glasgow coma scale, and volume of haemorrhage based on CT scan and location of haemorrhage.
For a Long time, serum ferritin was measured only to know the stored Iron status. Now it has been recommended that it influences the prognosis of ischemic stroke 1 and also acts as a risk factor for ischemic episodes by enhancing atherogenesis. 2, 3 In our study serum ferritin is assessed to evaluate the neurological deterioration and prognosis in patients of acute stroke. Therefore, measuring of serum ferritin is useful in identifying high risk patients.
Objectives
To study the effect of level of serum ferritin with early neurological deterioration and the outcome in patients of acute stroke.
Association of serum ferritin in ischemic and haemorrhagic stroke.
Study setting
This study was be done at Sri Manakula Vinayagar Medical College and Hospital (SMVMCH), Puducherry, under the department of General Medicine during the year 2018-20 after getting institution ethics committee approval. This is a hospital based analytical cross-sectional study. Sample size of this study was 50.
Exclusion criteria
Patients with anaemia.
Patients with history of malignancy.
Patients with liver disease or renal disease.
Patients with recent myocardial infarction within < 4 weeks.
Patients with history of previous stroke or intracranial haemorrhage.
Patients with k/c/o of rheumatoid arthritis or SLE.
Patients with h/o of fever.
Patients presenting after 48 hrs of onset of symptoms.
Study procedure
50 patients with acute stroke were selected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. Appropriate questionnaire was used to collect data of patients. Diagnosis of stroke was confirmed by CT or MRI scan of brain plain and examination was done by Canadian stroke scale at the time of admission. About 5ml of venous blood Sample from cubital vein was collected for measuring serum ferritin levels, it was performed within 48hrs of onset of symptoms by using CLIA method. Neurological assessment was repeated on the day of discharge to assess the clinical improvement and prognosis of the stroke patients.
The data obtained from the proforma was entered into Microsoft excel and analysed using statistical package for social sciences version 16. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Table 1 shows the distribution of the demographic characteristics of the patients with stroke. Majority of the patients were belonging to the age group of 51-60 years (36%) and were males (70%).
Table 2 shows the distribution of the behavioral risk factor profile of the patients. More than one-third of the patients were smokers (38%) and consuming alcohol (36%).
Table 3 shows the distribution of the comorbidities among the patients. Nearly half of the patients had diabetes mellitus, 52% had hypertension and 8% had cardiovascular disease.
Table 4 shows the distribution of serum ferritin levels among the patients with stroke. About 18% of the patients had high serum ferritin levels. The median serum ferritin value is 101.60 mg/dl.
Table 5 shows the lipid profile and the distribution of biochemical parameters among the stroke patients. About 18%, 38%, 10%, 14% and 30% patients had high cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and VLDL cholesterol, respectively.
Table 6 shows the distribution of stroke profile of the patients. Majority (90%) of the patients had ischaemic type of stroke while only 6% showed haemorrhagic transformation. Anterior circulation vessels were affected in most (74%) of the patients and more than half (52%) presented hemiplegia on the right side. Carotid stenosis was present in 6% of the patients while it was not done in 64% of patients.
Table 7 shows the Canadian stroke scale interpretation on the day of discharge among the stroke patients. The stroke scale status deteriorated in 20% of the patients while remained the same in majority (66%) of the stroke patients.
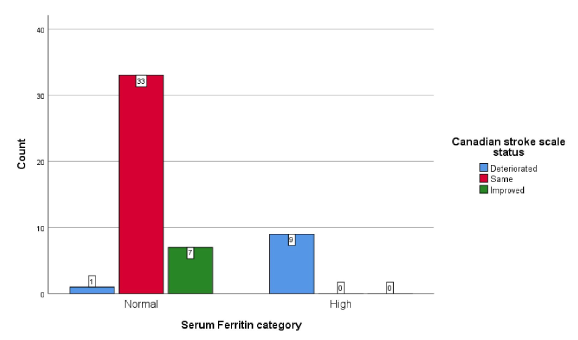
Table 8 shows the association and distribution of the serum ferritin levels with Canadian stroke scale status.High serum ferritin levels have been significantly associated with deterioration in Canadian stroke scale status (p<0.001) when compared to those with normal serum ferritin levels.
Figure 2 shows the association and distribution of the serum ferritin levels with Canadian stroke scale status. High serum ferritin levels have been significantly associated with deterioration in Canadian stroke scale status (p<0.001) when compared to those with normal serum ferritin levels.
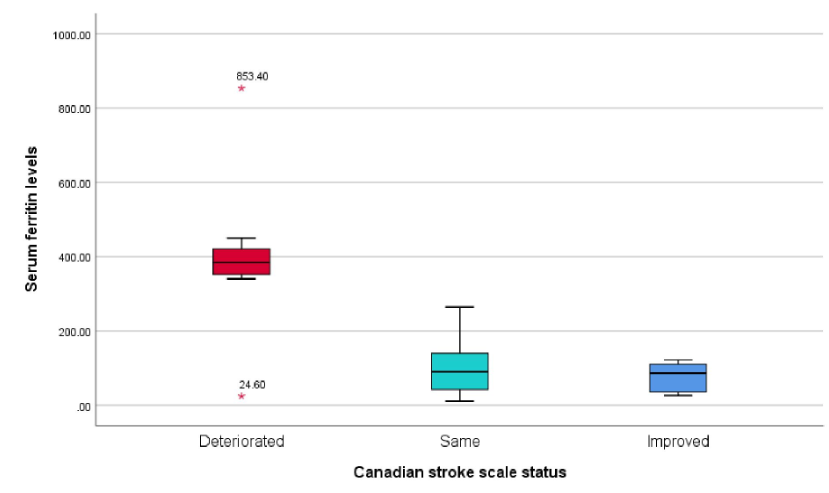
Table 9 shows the association and distribution of the serum ferritin values with Canadian stroke scale status. Those withdeteriorated Canadian stroke scale status had significantly high serum ferritin levels (p<0.001) when compared to other status groups. Canadian stroke scale status groups.
Figure 3 shows the association and distribution of the serum ferritin values with Canadian stroke scale status. Those with deteriorated Canadian stroke scale status had significantly high serum ferritin levels (p<0.001) when compared to other status groups. Canadian stroke scale status groups.
Table 1
Baseline demographic characteristics of the patients (n=50)
|
Variable |
Categories |
Number |
Percentage |
|
Age category |
≤50 years |
7 |
14 |
|
51-60 years |
18 |
36 |
|
|
61-70 years |
15 |
30 |
|
|
>70 years |
10 |
20 |
|
|
Gender of the patient |
Male |
35 |
70 |
|
Female |
15 |
30 |
Table 2
Behavioral risk factor profile of the patients (n=50)
|
Variable |
Categories |
Number |
Percentage |
|
Smoking status |
Yes |
19 |
38% |
|
No |
31 |
62% |
|
|
Alcohol consumption |
Yes |
18 |
36% |
|
No |
32 |
64% |
Table 3
Morbidity profile of the patients (n=50)
|
Variable |
Categories |
Number |
Percentage |
|
Diabetes Mellitus |
Present |
23 |
46% |
|
Absent |
27 |
54% |
|
|
Hypertension |
Present |
26 |
52% |
|
Absent |
24 |
48% |
|
|
Heart disease |
Present |
8 |
16% |
|
Absent |
42 |
84% |
Table 4
Serum ferritin profile of the patients (n=50)
|
|
Serum ferritin |
|
|
Levels, n(%) |
Normal |
41(82) |
|
High |
9(18) |
|
|
Mean (SD) |
161.07(160.73) |
|
|
Median (IQR) |
101.60(42.43-233.70) |
|
Table 5
Lipid profile of the patients (n=50)
Table 6
Distribution of stroke profile of the patients (n=50)
Table 7
Canadian stroke scale interpretation on the day of discharge (n=50)
|
Variable |
Number |
Percentage |
|
|
Canadian stroke scale status |
Deteriorated |
10 |
20% |
|
Same |
33 |
66% |
|
|
Improved |
7 |
14% |
|
Table 8
Association of the serum ferritin levels with Canadian stroke scale status (n=50)
|
|
Canadian stroke scale status |
Chi-square (p value) |
|||
|
Deteriorated |
Same |
Improved |
|||
|
Serum Ferritin category |
Normal |
1 (2.4) |
33(80.5) |
7(17.1) |
43.902 (<0.001) |
|
High |
9 (100.0) |
0 |
0 |
||
Discussion
This study was done to find the association of serum ferritin as a prognostic factor in acute cerebrovascular accident. The sample size of this study is 50, who are admitted under general medicine and neurology department in Sri Manakula Vinayagar medical college and hospital. Serum ferritin and neurological assessment by Canadian stroke scale was done in all patients. The sample size of this study was nearly equal to the study conducted by SK Mandal, Ashlian Kusvuran Ozkan et al.4
In this study it is observed that majority of the subjects are males 35 (70%), and females are 15(30%), and 36% were in the age group of 51-60 years, 30% between 61-70 years of age group and 20% is more than >70 years, and 14% are age less than 50 years. So, in this study majority of the stroke patients are in the age group of 51-60 years.
Similar study was conducted by Dr.Siddharth Kapoor et al, it was a prospective cohort study in that study 23 stroke patients were selected. In which males were 60.86% and females were 39.14%, majority of the subjects were in the age group of 51-60 years. Another study which was conducted by Hemant Mahur et al., 5 in that study males were 59.67% and females were 30.62% which is similar to our study. But in our study age and gender is not significantly associated with serum ferritin levels and Canadian stroke scale. In our study 38% of the subjects are smokers and 64% are alcoholics. Only alcohol consumption was significantly associated (p=0.034) with higher serum ferritin levels and with deterioration of Canadian stroke scale status. A study done by Elizabeth Mostofsky et al., 6 showed that heavy alcohol consumption increases the risk of stroke. In our study, out of 50 subjects 46% had diabetes mellitus and 52% had hypertension. Among them three diabetic patients and five hypertensive patients had high ferritin levels. A study of clinical profile of stroke was done by Daad H Akbar et al., 7 to determine the pattern and risk factors of stroke in Saudis and non-saudis population, it showed hypertension is the more common risk factor for both ischæmic and hemorrhagic stroke. In our study among 50 subjects 26 patients had hypertension but there is no positive correlation between serum ferritin and Canadian stroke scale status with diabetes and hypertension. The mean duration of both diabetes and hypertension is 5 years.
In this study Out of 50 patients, the 8 patients (16%) are diagnosed to have heart disease. About 14% of the patients had coronary artery diseases and 2% have valvular heart disease. There was no significant correlation of heart disease with serum ferritin and Canadian stroke scale status. None of the lipid profile parameter were significantly associated with serum ferritin and Canadian stroke status which is similar to the study done by Joshua Z. Willey et al. 8 In our study ischemic stroke was seen in 45 (90%) of the patients and 5 (10%) were seen in hemorrhagic stroke. The serum ferritin levels were found to be normal in 41(82%) subjects and were high in 9(18%) subjects. The mean ferritin level was 161.07ng/mL. Those patients with hemorrhagic stroke 60.0% had significantly higher ferritin levels and higher deterioration in Canadian stroke scale status (p=0.041) when compared with ischemic stroke. A study done by Yee Sien Ng et al., 9 the study showed. That the incidence of anterior circulation stroke is twice that of posterior circulation and small vessel stroke which is similar to our study. None of the stroke profile parameter like types of stroke and vessel affected were significantly associated with serum ferritin level and Canadian stroke scale status. 10 The Canadian stroke scale interpreted at the time of discharge to assess the prognosis of the patient from initial status shows deterioration in 20% of the patients and 66% of the patients remained in the same status and 14% of the patients were improved.
Association of serum ferritin levels with Canadian stroke scale status
Among 50 patient serum ferritin levels are normal in 82% and high in 18%. The mean serum ferritin level is 161.07. The Canadian stroke scale interpretation at the time of discharge showed 20% of the patients are deteriorated, 66% are under same status and 14% of the patients are improved. Those patients with hemorrhagic stroke had significantly higher serum ferritin level (60.0%) p=0.010 when compared with those of ischemic stroke (13.3%). Hemorrhagic stroke patients (60.0%) had higher deterioration in Canadian stroke status when compared with ischemic stroke (15.6%). Association of serum ferritin levels with Canadian stroke scale shows that high serum ferritin levels have been significantly associated with deterioration in Canadian stroke status (p<0.001) when compared to those with normal serum ferritin levels. The mean serum ferritin levels are higher in deteriorated patients 199.29% when compared to other Canadian stroke scale status groups.
Conclusion
This study is a cross sectional study, of association of serum ferritin as a prognostic marker in acute cerebrovascular accident.
This study showed that among 50 subjects, only 9(20%) patients have high serum ferritin levels. The serum ferritin levels are high in hemorrhagic stroke (60.0%) when compared to ischemic stroke (13.3%). In Canadian stroke scale status higher deterioration was seen in hemorrhagic (60.0%) stroke when compared with ischemic stroke (15.6%). In this study we had only minimal number of patients have hemorrhagic stroke (10%) hence association cannot be accurate.
This study showed that the significant rise in serum ferritin levels in hemorrhagic stroke patients it correlates with decrease score in Canadian stroke scale (CSS) which indicates the severity. The mean serum ferritin levels are higher in deteriorated patients 199.29% when compared to other Canadian stroke scale status groups.
Elevated serum ferritin levels have been significantly associated with deterioration in Canadian stroke scale status (p<0.001) when compared to those with normal serum ferritin levels. It reveals the poor outcome in patients with high serum ferritin levels.
This study shows male predominant, more patients with in the age group of 51-60 years.
Only alcohol consumption was significantly associated (p=0.034) with higher serum ferritin levels and with deterioration of Canadian stroke scale status.