- Visibility 206 Views
- Downloads 74 Downloads
- Permissions
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijn.2024.005
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Connectomic deep brain stimulators in Parkinson`s sub cortical functional zones
- Author Details:
-
Venkateshwarla Rama Raju *
Abstract
Background: Shaking palsy is a brain disease involving motor and non motor zones affecting circa 1 to 2%of humans>60 years age. To date there has been no invention for curing this chronic disease and to stop its progression. But existing therapeutic procedures can offer symptomatic relief to Parkinson patients. DBS is most successful therapy for the Parkinson`s yet depends on the accuracy of electrode implantation and location within the anatomical subcortical neural-structures.
Purpose: This study examines the likelihood of net-work-based induced stimuli and the application of connectomic DBS in Parkinson`s.
Materials and Methods: The subthalamic nucleus is divided into3 sub zones, namely, limbic (anterior), associative (middle) and motor (posterior) as well as diffusion weighted imaging (D W I). The surgical targets are tiny (few millimeters) and good enough to neuroanatomical-structures within the b r a i n. STN (size:12×5×3mm3) and lies nearby internal capsule, medial lemniscus, corticospinal tract, plus red-nucleus. Through sub optimal lead insertion and over stimuli, flow of electrons can spread to these adjoining sucortics, thereby developing dyskinesias ([Table 1] ). With time, DW-MRI plus f-MRI is used to study the anatomical-structural functional connectivity in advanced idiopathic Parkinson`s. Contrasting conventional lesion based stimulus hypothesis, the novel net stimulus hypothesis advocated that induced stimulus of exact circuits of b r a i n can modulate pathophysiological net-work, reinstate near the tissue region, thus producing stabilization-of human-brain-connectome within Parkinson`s.
Results: The DBS connectomes makes use of circuit based stimulus procedure instead of lesion-based stimulus, has transformed neuromodulation.
Conclusion: Connectomes via DBS can be tailor made for every Parkinson plus enhance the operation. It`s just a sketch for human-brain-connectivity (HMC) transversely compound longitudinal-scales. Yet, it won`t yield cell information plus cotacts with cells at the level of micro scale.
Introduction
Shaking palsy is a complex brain disease involving motoric and nomotoric zones affecting circa 1 to 2% of humans >60 years age. Normally, with L-dopa medication, Parkinson features and signs can be prevented for a limited period following the symptom onset prior to forming cardinal motor issues.[1], [2], [3] Device-based assistive remedies, particularly deep brain stimulators (DBS), was used in the direction and execution of advanced idiopathic PD when oral pharmacological deed is no longer adequate for the prevention of feature-manifestations so calmicroelectrode symptoms or whilst Parkinson`s not at all stand with the drug. [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9] To date there has been no invention for curing this complex malady and also to stop its progression. But existing therapeutic procedures can offer symptomatic relief to Parkinsons. DBS is most successful therapy for the Parkinson`s yet depends on the selection of suitable candidate, ideal point-of embedding electrode within the anatomical subcortical neural-structures, i.e., precision of location of leads plus optimum stimulus coding, also prescription (medicine) titration. [10], [11] A Okun and team testified that 46% of Parkinson`s through suggested stimulus failure were found to have suboptimal electrode implantation. Due to erratic implantation, 52% progressed after the reinsertion thoroughly [10] which focusses the significancy of accurate probe location in the perfection of DBS procedure.
Subthalamic—nuclei is the main surgical target object in Parkinson`s enduring DBS surgery.[12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18] Though brain stimulation to this object can upgrade motoric functioning and might cause a decline in dopaminergic medication dose, limited problems have been stated through embedding brain stimulators at STN zone. The STN though very tiny in diameter (few millimeters), is found to be segregated into functional sub zones.[19], [20], [21] Hence, even with the exact point of electrode, DBS candidates underwent surgery may get neuropsychiatric problems. Study[19] observed that the STN was distributed into three functional sub zones, namely, limbic (anterior), associative (middle) and motor (posterior) by the application of D W I. [19] Surgical targets are tiny (few millimeters) and good enough to neuroanatomical sub sections within b r a i n. As per the atlas, the STN (12×5×3mm3) lies nearby internals capsules, medial lemniscus, cortico spinal tract, plus red-nuclei. With suboptimal electrode insertion and over stimuli, so local-current reaches to nearby tissues, yielding dyskinesias (TABLE I).[22] Still STN may have little variance within the spot for current stimulation. [23] In contrast, lesions as of distinct locations (sub cortical regions) of brain might result in alike (analogous) parallel symptoms-features.[24] Thus, even if the point of contact of electrode is perfect, these target objects may vary during treatment.
Likewise, Parkinson`s have different symptoms, for instance, axial, motor and nonmotor, and symptoms subtypes as well. Therefore, brain stimulation at one target object of sub cortical sectors might not be good enough to alleviate symptoms—features.
|
Point of electrode Flow-of-current spread |
Functional structures (anatomical) pretentious |
Scientific (irrefutable) effects |
|
Optimum point |
Subthalamic nucleus |
Dyskinesia |
|
Very lower / medial |
Nervus oculomotorius structures |
Diplopia |
|
Very lateral / medial |
Medial lemniscus |
Paraesthesia |
|
Very frontal / horizontal |
Inner pill |
Stimulant muscular tissue shrinkage retrenchment |
|
Very frontal / horizontal |
Cortico spinal threads |
Dysarthria |
|
Very closely inferior |
Cerebello thalamic zone |
Ataxia |
|
Very inferior |
Substantia nigra (SN) |
Attitude (vein) difference |
For efficient control of symptoms, an idea hit in the scientists’ brains, and so they discovered the possibility of detecting the perfect points (sites) that are responsible for diseased symptoms and connecting t such points to form the circuit (or network). They showed that a therapeutic option is better, if and only if a route linking these points is sketched out for every diseased Parkinson, exciting the circuitry, instead of the conventional-fixed way of inducing the subcortical subthalamic-nuclei,[25], [26], [27], [28], [29], [30], [31], [32], [33], [34] the idea of connectome emerged. This article discusses the method of human and normative connectomes, the application of DBS connectomes brain stimulators inside the PD diseased conditions and neuro modulation surgery.
Materials and Methods
In line with the standard teaching teaching—principles, the location of abrasions within the central nervous system (CNS) accounts for maximum neurodegenerative feature-manifestations and we encountered certain limitations, such as lesion-based location is sporadically not clear.
Lesions generating identical symptoms can appear in diverse sections or organs of brain, while brain lesion can outcome in unlike neural signs. So, the correlation among neural-signs and point of lesion is seldom direct. [25], [26], [27] It`s not rare to have diseased subjects with composite and dense neural and neuropsychiatric signs inept for finding apparent yet discernible brain lesions as of neuroradiological imaging.[27] Thus, it has been gambmicroelectrode and ventured that these neural-signs, rather than resultant as of explicit yet palpable abrasions within the CNS, might be triggered by distraction of anatomical—structural also functional nets built by networking neural- components, that are at a above level of microscopics.
For understanding the nebulous human brain which consists of trillions of nerve cells circa ~ 10100 neurons, first we need to study – understand the concept of dynamical connectomes. Connectome can be defined as as a thorough fundamental sketch of the network such that the connections build the human brain like a complex circuit. [25], [26] Connectomes in general and at large have three major components, explicitly, sketch of anatomical-structures (different components, elements, organs and parts of the brain) and observes the set of physical-layers link amid neuronal elements. Plus, to observe the links (i.e., connections) relating neuronal components, we intend to look at structural brain as well as functional brain connectivity.
Structural brain connectivity gives a coherent anatomical explanation of structurally building connections in the CNS. At the meso and micro scales, structural brain connectivity uncovers the synaptic-connections (in other words point of contacts from one cell to another and from one neuron to another vis-à-vis and vice-versa) amid neural-cells or long-distance (running down the) axonal prognoses amongst neural populations [28], [29]. Conversely, at the macro scale, structural brain connectivity points to large, myelinated bundles of fibers of white-matter (and partially grey matter), which can be imagined through the data of DW-MRI with the help of certain specialized computer software, for e.g., tractography. [30], [31]
As far as functional brain connectivity, which means that connections in stimulation amongst spatially discrete regions-of-brains, whichever in a latent, i.e., resting state or through the exterior (peripheral) stimulations which can be evaluated as the bi variate correlations of their behaviors while applying the data of f-MRI. [26], [32], [33], [34]
Secondly, connectomes are only the connectivity-of-brain about compound spatial scales. But, this won`t give all cells information plus the point of contact-synapses at the levels-of micro scales. [26]
Finally, the connectome is how the elements of brain are connected through the description of neural-net. [26] Which means in neural nets each neuron sends impulses to many neurons calmicroelectrode divergency and similarly each neuron receives impulses from many neurons calmicroelectrode convergency and this information transmission mechanism in the human works through chemical messengers and neurons connecting from to another with which it builds the functional brain connectivity. Through the application of mathematical frameworks also statistical methods (computational simulation and statistical modeling) the connectome is simply an object target which hysterics or paroxysms in a greater hypothetical basis, thus connecting neuroscience to neural (and neuronal) network-science plus multifaceted complex neural engineering systems. [26]
Mapping human connectomes
Basically human connectome is the brains anatomical structural depiction of neural nets and connections through the point of contacts in which human memory lies (synapses) through many longitudinal-scales. As per the study,[26] there are three scales of structural-configurations orchestrated inside the brain: Single neurons and synapses at the micro scale level,[35], [36] neural populations together with their intersecting circuitry at the meso scale level, [37], [38], [39] anatomically distinct-structural zones of human-brain plus path ways. However, diagramming of connectomes initially primary and secondary stages generally appears in primates and is mostly done invivo experiments as trials. This study focuses primely on representing the human-brain connectome(HBC) at macro scale measurement levels. As we are all aware, MRI is a noninvasive imaging method that has long been used for mapping the brain’s comprehensive anatomical -connections within brain-tissues, [26], [27] plus we need to study the structural and functional connectivity.
Brain`s structural -connectivity is generally evaluated through DW-MRI sequences, after probabilistic tractography, since water molecules travels further easily laterally substantia alba (the white- substance) fiberebundles than transversely thus this substance paths can be rebuilt microelectrode, so detecting fibers which travels amid numerous brain-sector zones. [27]
By disparity, sleeping (i.e., in resting state) functional-MRI (sf-MRI) is often applied to examine the functional brain connectivity that observes the oxygen (O2) levels of blood/plasma conditional signal/waveform, which can serve like ancillary biomarker/signature of neural and/or neuronal behavior. [27], [34] Whilst the b r a i n action rises, the blood-flow plus consumption of glucose rise extremely above O2 ingesting. Thus, the amount of de-oxygenized hemoglobin reductions (i.e., reduce) within the area of improved action plus oxygenated O2 blood signal gets raised.[40] As mentioned earlier, functional brain connectivity is derived as the statistical linkage concerning time-domain series and sequences of structurally and/or functionally (i.e., anatomically) distinctive brain areas, in which f-MRI is predictably computed as zero-lag correlation (whilst functional brain connectivity is generally derived by applying the z e r o- l a g c o r r e l a t i o n). On the other hand, if brain areas, say two and/or left and right brain areas have oxygen (O2) levels of blood/plasma conditional signal which are concurrent, then they are linked functionally. [34]
Through the application of DW-imaging and f-MRI, functional-human brain (FBC) connectomes can be planned at macro scale levels.[25], [27] A human brain connectome procedure is defined in ([Figure 1]).[25]
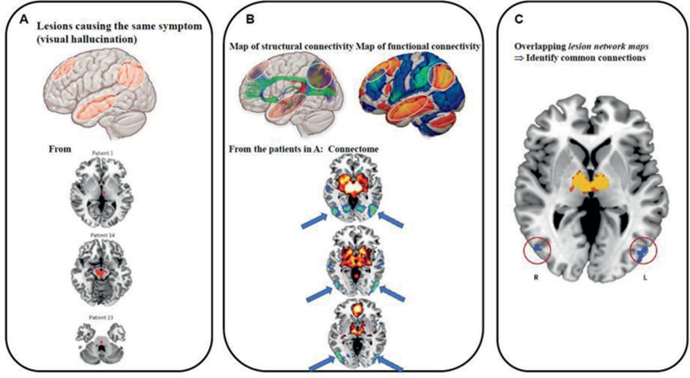
Step#1: After the predictive tractography of thalamo cortical tracts and cortico cortical internal real path ways, DW-MRI can be implemented to assist in parcellation of brain, and so building the v o x e l- w i s e predictive from many to many anatomical;-structural matric of brain connectivity.
Step#2: Then, a link of spatially measured sleeping-state and/or commission based fMRI logged within the identical candidate is then achieved to build a v o x e l- w i s e many to many functional brain connectivity to corresponding brain.
Step# 3: Consequently, the unsupervised clustering of correlations connecting the anatomical structural brain plus functional brain connectivity matrix achieved as of final two strides is done. Through which brain zones of reliable structure-role and meaning connections can be uncovered.
Thus, it`s feasible for mapping out the human brain connectome. For progressing the quality of results further we must match plus relate the represented net by primate-models for viewing the connection and variations. Likewise, the expectations produced from basic-efficient matrix connectivity can be proven through the explicitly induced stimulus techniques.
Normative and human brain connectomes
While human brain connectomes are a great steps for improving the location within CNS, it is cumbersome, classy plus might be fatiguing to the diseased as they must go by a long-lasting method of image gatherings through imaging modalities (such as the DW-fMRI, and fMRI). Certainly, the scientific experimental image setting, brain connectome can be experimented using separate image data as of a group of candidates (diseased) which gives a clue termed as normative brain connectome (NBC), that elucidated as a regular or comprehensive yet widespread connecting (wiring) map of brain.[27] NBC is applicable to those who are vain to acquire self-connectomes.[27] For example, in Parkison`s by acute shake or side-effect and when unable to get clarity images with no motion and all kinds of noise artifacts and through cerebral lesions, e.g., cerebrovascular catastrophe, they might not get self-connectomes, albeit, they can endure the long process imaging Due to the earlier findings of cerebral rational detaimicroelectrode areas of brain in the brain might have injured, so disorderly the circuitry is which is centrally also making it incredible to plan the efficient brain connectivity exactly. But normative connectome acquired from the imaging data, cannot give every single data connectivity of self-brain and thus might not signal his real condition. Due to the oldage, sex, b o d y-mass i n d e x(BMI) plus neurodegenerative disorders[41], [42], [43], [44], [45], [46] it can vary.
Intrinsically, for studying the normative brain connectome research clinically and technically, regarding normative connectome, it has been increasing with the introduction of human connectome project (HCP) of America. A massive indeed big project piloted in America to observe circuits of brain plus its link to activities in a big normal controls yet aged population at the macro-scopic test level.[27], [47], [48] Some data of neuro imaging and clinical info gathered from HCP is given below. [47], [48], [49]
Multimodal neuroimaging with 7 and 10T-MRIs: underlying, managing, also DW-MRI, Magnetoencephalography(MEG), Genetic-analyses, followed by developmental evaluation.
Results and Discussion
Uses of NBC and deep brain stimulations
As discussed so much about the normative brain connectome (NBC), it is a robust and vigorous tool for studying the complex network within the brain and can be applied in many distinct areas.
Firstly, NBC can uncover the basic intricate and problematic pathways of many neural and neurodegenerative diseases and neuropsychiatric disorders which can give good intuitions to the discovery of novel therapeutic targets. Consider [Figure 1] as an illustration. Mapping connectomes onto the group of patient population having visual hallucinations, abrasions that source the signs were uncovered to be linked to occipital-cortex which helps in the detection of new therapeutic-targets, the repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulations(r-TMS) on occipital-cortex can overwhelm visual illusions or hallucinations or vision. [50]
Secondly, NBC can improve clinical accuracy, so recover medical effect of various neural processes. Like, patients of gliomas planning for surgical procedure, use of NBC can aid in the detection of moving regions plus motoric-tracts prior surgery, thus dipping numerous intra op induced stimuluses’ mandatory to securely authorize the tract, reducing the possibility of disorderly epileptic-seizures, dropping the hazards and perils of post op neural discrepancies, simplifying the resection, plus making diseased subjects further easy in the surgery. [51], [52] Epileptic-surgery can be considered as with good another illustration. It is showed that by the application of connectomes, the result of epileptic-surgery can be recovered plus threats of post op neuro cognitive sequelae, with cognitive impairment (CI), cognitive dementia (CD), memory, language and semantic weakening, verbal linguistic problems can be concentrated. [53], [54], [55], [56]
Finally, NBC is largely applied in neuromodulation, mainly conventional open as well as closed loop adaptive D B S devices. Hypothetically, the D B S device functions through depolarization zone, synaptic-inhibition, melancholy like depression, and stimulus-induced-modulations of patho-physiological networks movements thought the very focal method of activity.[57], [58] So, once NBC lets us plan the (patho) physiological path ways within brain, the stimuli at convinced or selected points by the circuitry might re-establish the interrupted information flow and thus ease the subjects’ signs and symptoms and syndromes too. Also, implanted pulse generators that works as innocuous wires. i.e., micro electrodes, might develop s e e d s/or regions – of -interest (RoI) once they are applied to compute their connectivity outlines through NBC to infer network-based analysis. By this way, we may discover the optimum, most select-site (point of contact) for stimulus plus prevent adverse dyskinesias, so accelerating DBS coding and also adjusting accurate clinical-outcome. [59]
The process of connectomes and deep brain stimulators implantation
Believing that big contrast amid the diseased brain plus normal one, NBC examination can be performed to study the diseased connect report with which his implanted pulse generators (i.e., neuro stimulators) might modulate. Distinct single connectomic-DBS investigation, any anatomical(structural) or data of fMRI is good-enough for NBC evaluation. On the other hand, any DW-MRI through tractography or fMRI is mandatory for NBC assessment. Through this complex scrutiny, the accuracy of pre op targeting plus post op DBS programming might be improved. [23], [60], [61] The procedure to perform connectomic-DBS investigation in Parkinson`s implanted pulse generators is explained ([Figure 2]). [23], [60], [61]

Coregistration
Prior to the operation, all the Parkinson`s must register for MRI or fMRI and DW-MRI and then screening is done accordingly. Following the operation, the computed axial tomography (CAT) is accomplished. Postop CAT candidate is then co-registered by pre op magnetic resonance imaging importantly by the brain shift adjustment (if any) plus normalizing the data spatially.
Location of electrode (point of electrode contact)
Following the registrations of pre op and post op neuroimaging MRI, fMRI or DW-MRI, the probes can be located whilst the contiguous neuro anatomical shapes are labemicroelectrode.
Predicting VTA
The volume of tissue activation, i.e., VTA is the estimation of volume plus identity of distributing stimulus pulse generators while link over the DBS MICROELECTRODE is stimulated which varies over the configuration settings of signal generator, for instance point of contact, ohmic resistance (the impedance), electrical-current voltage, i.e., stimulus intensity pulse-width and frequency[62], [63] which are parameters of the DBS. Localize
Following the confinement of microelectrodes, the VTA is predicted through stimulated connection(s) over the microelectrodes detected. Neuroscientists can decide the point of contacts of electrodes that are stimulated through the mono polar stimuli and choose the deep brain stimulations and the setup. So, VAT can be predicted as per the parameters of DBS coding.
Estimating the connectivity silhouette
Once the region-of-interest (ROI) is detected then the same might be utilized like the seed in the identifiable anatomical— NBC to perform its efficient structural connectivity. Mostly, VTA of the pulse generator stimulating lead details is chosen like a seed.
DBS connectomes and clinico-statistical findings
Lastly, clinic statistical tests were done to examine if there is a connection relating to the placement of the electrode connectivity also clinic-prognosis and prognostic results, and that can be cardinal-symptoms progression or dyskinesias.
|
Researchers work on |
Device targets |
# of Subjects |
Connectome Type |
Outcome |
|
Paraphernalia of motor |
|
|
|
|
|
H o r n, et.,al., [23] |
STN |
5 1 |
SBC |
VTAs linking for EMA associated to experimental motoric progress |
|
T r e u, et.al.al., [61] |
STN |
5 1 |
SBC |
VTAs linking for M1 / S1 adversely (-Ve) associated by outcome of motor. |
|
Horn, et al., [45] |
S T N |
94 |
SBC |
VTA SBC by |
|
|
|
|
|
EMA linked through medical motor progress |
|
|
|
|
|
FBC by M1 linked through clinical-motor progress. |
Connectomes and DBS in Parkinson`s
Certainly, utilization of human-brain connectome(HBC) examined greatly within neuromodulation, specifically in key indications like Parkinson`s disease and movement disorders. Overall, electrode-point is most significant in the success. Usually, lesion-based location at precise targets, that is subthalamic-nuclei is more found to progress the cardinal motor sign in Parkinson`s. Yet, further studies have explored the link amid connectivity-based site plus therapeutic results of the stimulus device, i.e., DBS, as improving signal indicates that the stimulus device functions by reinstating the connectivity of irregular networks corresponding to the functional biological state.[57], [58] Studies[23], [45], [59], [60] stated that through the application of normative brain connectome(NBC), anatomical-structural brain connectivity (A-SBC) to the extra motor area (EMA), more anterior-gyrus plus cerebellum were linked by useful irrefutable retort, anatomical structural brain and functional brin connectivity(FBC) were autonomous prognosticators of irrefutable upgrading of STNDBS. [45]
Then, it`s assumed that, if distinct operating targets can modulate the equal circuitry in Parkinson’s plus alter therapeutics outcome. In a study,[64] the researchers presented that based on normative connectome atlas(NCA), connectivity silhouettes sowing as of STNDBS implanted pulse generators (IPGs) electrodes were verylike, signifying that regardless of target, the net-work modulated by the therapeutic surgical device considerably overlap. [64] Furthermore, in two cohorts, FBC to the ‘frontal-lobes’, EMA plus adjoining cingulate, central plus mediocre temporal-gyri, mediocre parietal-gyri also motoric cerebellum was correlated with safe experimental findings [64]. On the other hand, although they showed resemblance within the circuit modulated by stimulus devices, the therapeutic reaction in two cohorts altered. For the cardinal motoric symptoms, tremor, rigidity and akinesia, connectivity outline was correlated by major progression plus mutually substantial resemblance in two cohorts. In differ, the findings for cardinal motor tremor symptom was dissimilar, implying that the networks modulated by actual stimuli at altered targets, although analogous, might have a slight difference.[64]
It is well known that the since long electro neuro physiological data utilized like biomarkers to the abrasion-based neuro modulation device-based operations, i.e., DBS procedures’ in Parkinson`s. For instance, local current distribute field potentials(i.e., field-potentials, i.e. locally distributed LFPs) might act as the device for sensing brain within Parkinson`s using DBS device electrodes which are embedded over the STN, so enabling the programming with DBS device plus treatment titration. The improved β oscillatory activities were detected in the hypo dopaminergic-state while diseased ache from cardinal motoric symptoms, akinesia, stiffness, and might be repressed with the therapeutic device (DBS) plus dopamine medical management. In contrast, the enhanced γ oscillations activities were viewed during the side-effects[65], [66], [67], [68], [69] Yet, in diseased through connectivity based stimuli, will the electro neuro physiological data relate through connectivity outline? In a study, researchers[70] labelmicroelectrode that β oscillations were noticed within cerebral (logical) circuitry jutting as of subthalamic-nuclei to motoric plus pre motoric, i.e., motor cortical (motor cortex) zones within Parkinson`s. [70] Also, in an another study, researchers stated that using magneto encephalo-graphy(MEG), field potentials also electro-myo-graphy(EMG), raised β-coherence (logical) was create amid M1 plus sub thalamic within the Parkinson`s diseased conditions, that could be with the medical management of L-dopa. Our results showed that the connection amongst electro neuro physiology data plus connectivity based stimuli.
Intrinsically, connectomic-DBS looks like rational also effective therapeutic option to advanced idiopathic neurodegenerative Parkinson disease patients. Increasing indication has presented that reliant over the signs, connectomic-minimally invasive DBS surgical-procedure can turn on different circuitry within the brain. Thus, neuromodulation DBS operation might impact over motoric and nonmotor dos ([Table 2]). [23], [45], [61]
Conclusions
To conclude, in summary connectomic-DBS, that makes application of circuit-based stimulus method instead of lesion based stimulus method, has modernized and transformed neuromodulation. Through the stimulation of patient specific circuits, DBS-based therapeutic surgery allows us to give a further precise medical admin method whilst preventing adverse dyskinesias. Furthermore, through the advent of NBC obtained via clustered data, it`s cutdown the complex process of brain-connectome mapping, trajectory planning plus coding of DBS device, compelling it further accessible and intelligent to the neuroscientists and brain connectomes-planning support us to sketch the feature-symptoms and signs individual circuitry for every candidate exclusively also examine for the intersect of this circuitry. Thus, DBS-connectomes, i.e., minimally invasive operation can be tailormade for every diseased as well as suited customized personalized surgery which might address their personal demands.
Conflict of Interests
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Kalia L, Lang A. Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2015;386(9996):896-912. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner C, Aston D. Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease and akinetic syndromes. Curr Opin Neurol. 2000;13(4):427-30. [Google Scholar]
- Aquino C, Fox S. Clinical spectrum of levodopa-induced complications. Mov Disord. 2015;30(1):80-9. [Google Scholar]
- Worth P. When the going gets tough: How to select patients with Parkinson's disease for advanced therapies. Pract Neurol. 2013;13(3):140-52. [Google Scholar]
- Volkmann J, Albanese A, Antonini A, Chaudhuri K, Clarke C, Bie RD. Selecting deep brain stimulation or infusion therapies in advanced Parkinson's disease: an evidence-based review. J Neurol. 2013;260(11):2701-14. [Google Scholar]
- Williams D, Evans A, Fung V, Hayes M, Iansek R, Kimber T. Practical approaches to commencing device-assisted therapies for Parkinson disease in Australia. Intern Med J. 2017;47(10):1101-13. [Google Scholar]
- Moro E, Lang A. Criteria for deep- brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: Review and analysis. Expert Rev Neurother. 2016;6(11):695-705. [Google Scholar]
- Defer G, Widner H, Marié R, Rémy P, Levivier M. Core assessment program for surgical interventional therapies in Parkinson's disease (CAPSIT-PD). Mov Disord. 1999;14(4):572-84. [Google Scholar]
- Munhoz RP, Picillo M, Fox SH, Bruno V, Panisset M, Honey CR. Eligibility criteria for deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease, tremor, and dystonia. Can J Neurol Sci. 2016;43(4):462-71. [Google Scholar]
- Okun M, Tagliati M, Pourfar M, Fernandez H, Rodriguez R, Alterman R. Management of referred deep brain stimulation failures: A retrospective analysis from two movement disorders centers. Arch Neurol. 2005;62(8):1250-5. [Google Scholar]
- Limousin P, Foltynie T. Long-term outcomes of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(4):234-42. [Google Scholar]
- Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Schäfer H, Bötzel K. German Parkinson study group, Neurostimulation section. A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease. New Engl J Med. 2006;355(9):896-908. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver F, Follett K, Stern M, Hur K, Harris C, Marks W. Bilateral deep brain stimulation vs best medical therapy for patients with advanced Parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;301(1):63-73. [Google Scholar]
- Okun M, Fernandez H, Wu S, Kirsch-Darrow L, Bowers D, Bova F. Cognition and mood in Parkinson's disease in subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation: The COMPARE trial. Ann Neurol. 2009;65(5):586-95. [Google Scholar]
- Follett K, Weaver F, Stern M, Hur K, Harris C, Luo P. Pallidal versus subthalamic deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(22):2077-91. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver F, Follett K, Stern M, Luo P, Harris C, Hur K. Randomized trial of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: thirty-six-month outcomes. Neurology. 2012;79(1):55-65. [Google Scholar]
- Odekerken V, Laar TV, Staal M, Mosch A, Hoffmann C, Nijssen P. Subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus bilateral deep brain stimulation for advanced Parkinson's disease (NSTAPS study): A randomised controlmicroelectrode trial. Lancet Neurol. 2012;12(1):37-44. [Google Scholar]
- Odekerken V, Boel J, Schmand B, Haan RD, Figee M, Munckhof PVD. GPi vs STN deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: Three-year follow-up. Neurology. 2016;86(8):755-61. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert C, Zrinzo L, Nagy Z, Lutti A, Hariz M, Foltynie T. Confirmation of functional zones within the human subthalamic nucleus: Patterns of connectivity and sub- parcellation using diffusion weighted imaging. NeuroImage. 2011;60(1):83-94. [Google Scholar]
- Benarroch E. Subthalamic nucleus and its connections: Anatomic substrate for the network effects of deep brain stimulation. Neurology. 2008;70(21):1991-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ewert S, Plettig P, Li N, Chakravarty M, Collins D, Herrington T. Toward defining deep brain stimulation targets in MNI space: A subcortical atlas based on multimodal MRI, histology and structural connectivity. NeuroImage. 2017;170:271-82. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Krack P, Fraix V, Mendes A, Benabid A, Pollak P. Postoperative management of subthalamic nucleus stimulation for Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2002;17( Suppl 3):188-97. [Google Scholar]
- Horn A, Li N, Dembek T, Kappel A, Boulay C, Ewert S. Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. NeuroImage. 2018;184:293-16. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Karnath H, Sperber C, Rorden C. Mapping human brain lesions and their functional consequences. NeuroImage. 2017;165:180-9. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Sporns O, Tononi G, Kötter R. The human connectome: A structural description of the human brain. PLoS Comput Biol. 2005;1(4). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Sporns O. The human connectome: A complex network. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1224:109-25. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Fox M. Mapping symptoms to brain networks with the human connectome. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(23):2237-45. [Google Scholar]
- Oh S, Harris J, Ng L, Winslow B, Cain N, Mihalas S. A mesoscale connectome of the mouse brain. Nature. 2014;508(7495):207-14. [Google Scholar]
- Markov N, Ercsey-Ravasz M, Gomes AR, Lamy C, Magrou L, Vezoli J. A weighted and directed interareal connectivity matrix for macaque cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex. 2012;24(1):17-36. [Google Scholar]
- Basser PJ, Pajevic S, Pierpaoli C, Duda J, Aldroubi A. In vivo fiber tractography using DT-MRI data. Magn Reson Med. 2000;44(4):625-32. [Google Scholar]
- Daducci A, Gerhard S, Griffa A, Lemkaddem A, Cammoun L, Gigandet X. The connectome mapper: An open-source processing pipeline to map connectomes with MRI. PLoS One. 2012;7(12). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Zhou D, Thompson WK, Siegle G. MATLAB toolbox for functional connectivity. NeuroImage. 2009;47(4):1590-607. [Google Scholar]
- Smith S, Miller K, Khorshidi GS, Webster M, Beckmann C, Nichols T. Network modelling methods for FMRI. NeuroImage. 2010;54(2):875-91. [Google Scholar]
- Pervaiz U, Vidaurre D, Woolrich M, Smith S. Optimising network modelling methods for fMRI. NeuroImage. 2020;211. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- White J, Southgate E, Thomson J, Brenner S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986;314(1165):1-340. [Google Scholar]
- Chen B, Hall D, Chklovskii D. Wiring optimization can relate neuronal structure and function. PNAS. 2006;103(12):4723-8. [Google Scholar]
- Micheva K, Smith S. Array tomography: A new tool for imaging the molecular architecture and ultrastructure of neural circuits. Neuron. 2007;55(1):25-36. [Google Scholar]
- Palm C, Axer M, Gräßel D, Dammers J, Lindemeyer J, Zilles K. Towards ultra-high resolution fibre tract mapping of the human brain -registration of polarised light images and reorientation of fibre vectors. Front Hum Neurosci. 2010;4. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Axer M, Amunts K, Grässel D, Palm C, Dammers J, Axer H. A novel approach to the human connectome: Ultra-high resolution mapping of fiber tracts in the brain. NeuroImage. 2009;54(2):1091-101. [Google Scholar]
- Fox M, Raichle M. Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(9):700-11. [Google Scholar]
- Christova P, James L, Georgopoulos A. Effects of sex and age on presumed inhibitory interactions in 6 areas of the human cerebral cortex as reveamicroelectrode by the fMRI human connectome project. Exp Brain Res. 2022;240(3):969-79. [Google Scholar]
- Kim H, Shin N, Nam Y, Yun E, Yoon U, Lee H. MRI-visible dilated perivascular space in the brain by age: The human connectome project. Radiology. 2022;306(3):1-9. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- CF, Jha M, Minhajuddin A, Mayes T, MT. Sex-specific differences in the association between body mass index and brain aging in young adults: Findings from the human connectome project. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020;124. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Wang Q, Akram H, Muthuraman M, Gonzalez-Escamilla G, Sheth S, Oxenford S. Normative vs. patient- specific brain connectivity in deep brain stimulation. Neuroimage. 2020;224. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Horn A, Reich M, Vorwerk J, Li N, Wenzel G, Fang Q. Connectivity predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol. 2017;82(1):67-78. [Google Scholar]
- Germann J, Elias G, Boutet A, Narang K, Neudorfer C, Horn A. Brain structures and networks responsible for stimulation‐induced memory flashbacks during forniceal deep brain stimulation for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17(5):777-87. [Google Scholar]
- Essen DV, Smith S, Barch D, Behrens T, EY, KU. The WU-Minn human connectome project: An overview. NeuroImage. 2013;80:62-79. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Glasser M, Smith S, Marcus D, Andersson J, Auerbach E, Behrens T. The human connectome Project's neuroimaging approach. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19(9):1175-87. [Google Scholar]
- Elam J, Glasser M, Harms M, Sotiropoulos S, Andersson J, Burgess G. The human connectome project: A retrospective. NeuroImage. 2021;244. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Merabet LB, Kobayashi M, Barton J, Pascual-Leone A. Suppression of complex visual hallucinatory experiences by occipital transcranial magnetic stimulation: A case report. Neurocase. 2003;9(5):436-40. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson F, Abdullah K, Verma R, Brem S. Tractography and the connectome in neurosurgical treatment of gliomas: The premise, the progress, and the potential. Neurosurg Focus. 2020;48(2). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Chen Z, Ye N, Teng C, Li X. Alternations and applications of the structural and functional connectome in gliomas: A mini-review. Front Neurosci. 2022;16. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Taylor P, Sinha N, Wang Y, Vos S, Tisi JD, Miserocchi A. The impact of epilepsy surgery on the structural connectome and its relation to outcome. Neuroimage Clin. 2018;18:202-14. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Arski O, Martire D, Young J, Wong S, Suresh H, Kerr E. Connectomic profiles and cognitive trajectories after epilepsy surgery in children. Neurology. 2022;98(22):e2233-44. [Google Scholar]
- Chen X, Wang Y, Kopetzky SJ, Butz-Ostendorf M, Kaiser M. Connectivity within regions characterizes epilepsy duration and treatment outcome. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021;42(12):3777-91. [Google Scholar]
- Englot DJ, Konrad PE, Morgan VL. Regional and global connectivity disturbances in focal epilepsy, related neurocognitive sequelae, and potential mechanistic underpinnings. Epilepsia. 2016;57(10):1546-57. [Google Scholar]
- Mcintyre C, Savasta M, Goff LK, Vitek J. Uncovering the mechanism(s) of action of deep brain stimulation: Activation, inhibition, or both. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;115(6):1239-48. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano A, Lipsman N, Bergman H, Brown P, Chabardes S, Chang J. Deep brain stimulation: Current challenges and future directions. Nat Rev Neuro. 2019;15(3):148-60. [Google Scholar]
- Horn A, Ostwald D, Reisert M, Blankenburg F. The structural-functional connectome and the default mode network of the human brain. NeuroImage. 2013;102:42-51. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Horn A, Kühn AA. Lead-DBS: A toolbox for deep brain stimulation electrode locations and visualizations. Neuroimage. 2014;107:127-35. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Treu S, Strange B, Oxenford S, Neumann WJ, Kühn A, Li N. Deep brain stimulation: Imaging on a group level. NeuroImage. 2020;219. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Mädler B, Coenen V. Explaining clinical effects of deep brain stimulation through simplified target-specific modeling of the volume of activated tissue. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(6):1072-80. [Google Scholar]
- Dergachyova O, Zhao Y, Haegelen C, Jannin P, Essert C. Automatic preoperative planning of DBS electrode placement using anatomo-clinical atlases and volume of tissue activated. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2018;13(7):1117-28. [Google Scholar]
- Sobesky L, Goede L, Odekerken V, Wang Q, Li N, Neudorfer C. Subthalamic and pallidal deep brain stimulation: Are we modulating the same network?. Brain. 2022;145(1):251-62. [Google Scholar]
- Kühn A, Fogelson N, Limousin P, Hariz M, Kupsch A, Brown P. Frequency-specific effects of stimulation of the subthalamic area in treated Parkinson's disease patients. Neuroreport. 2009;20(11):975-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kühn A, Kempf F, Brücke C, Doyle L, Martinez-Torres I, Pogosyan A. High-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus suppresses oscillatory beta activity in patients with Parkinson's disease in parallel with improvement in motor performance. J Neurosci. 2008;28(24):6165-73. [Google Scholar]
- Tinkhauser G, Pogosyan A, Tan H, Herz D, Kühn A, Brown P. Beta burst dynamics in Parkinson's disease OFF and ON dopaminergic medication. Brain. 2017;140(11):2968-81. [Google Scholar]
- Kühn A, Tsui A, Aziz T, Ray N, Brücke C, Kupsch A. Pathological synchronisation in the subthalamic nucleus of patients with Parkinson's disease relates to both bradykinesia and rigidity. Exp Neurol. 2008;215(2):380-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kühn AA, Kupsch A, Schneider GH, Brown P. Reduction in subthalamic 8-35 Hz oscillatory activity correlates with clinical improvement in Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;23(7):1956-60. [Google Scholar]
- Accolla EA, Ruiz H, Horn M, Schneider A, Schmitz-Hübsch GH, Draganski T, et al. Brain networks modulated by subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Brain. 2016;139(9):2503-15. [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Raju VR. Connectomic deep brain stimulators in Parkinson`s sub cortical functional zones [Internet]. IP Indian J Neurosci. 2024 [cited 2025 Nov 01];10(1):22-29. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijn.2024.005
APA
Raju, V. R. (2024). Connectomic deep brain stimulators in Parkinson`s sub cortical functional zones. IP Indian J Neurosci, 10(1), 22-29. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijn.2024.005
MLA
Raju, Venkateshwarla Rama. "Connectomic deep brain stimulators in Parkinson`s sub cortical functional zones." IP Indian J Neurosci, vol. 10, no. 1, 2024, pp. 22-29. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijn.2024.005
Chicago
Raju, V. R.. "Connectomic deep brain stimulators in Parkinson`s sub cortical functional zones." IP Indian J Neurosci 10, no. 1 (2024): 22-29. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijn.2024.005
